Configuration of Git
Check if Git is installed
git --version
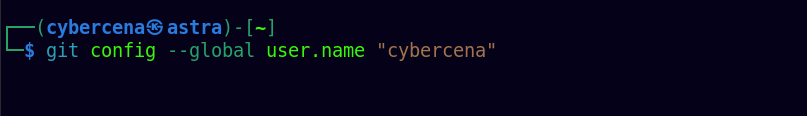
Configure Git Globally

Configure Git Locally
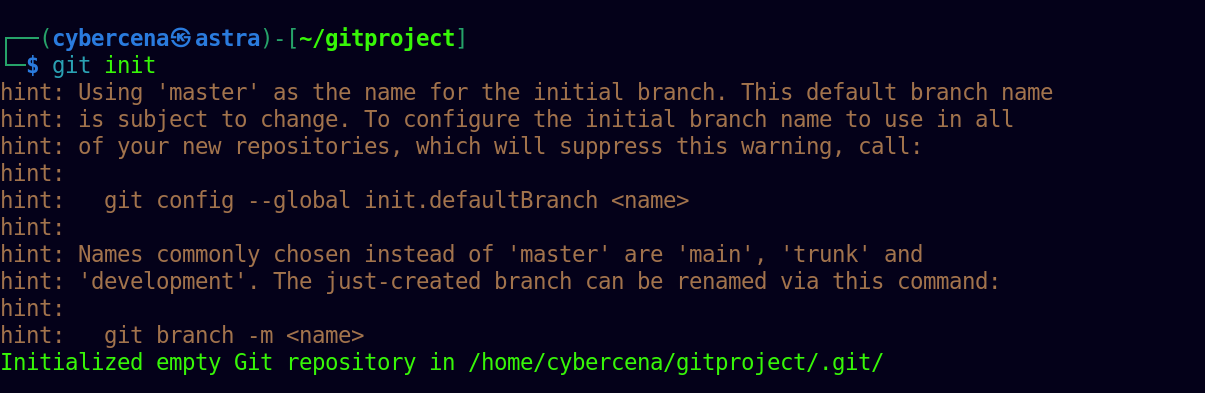
Step 1 : Create a Repository


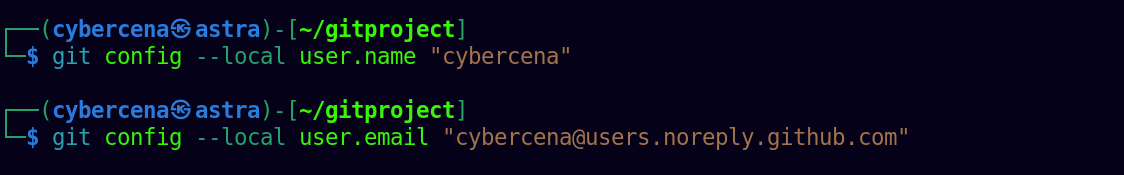
Step 2 : Configure the Git locally
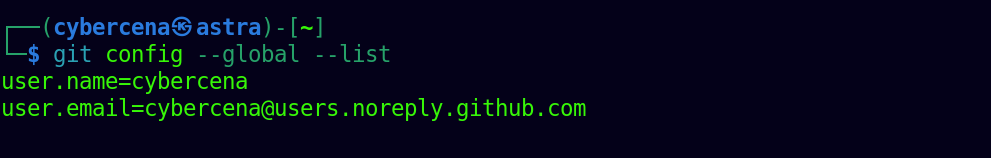
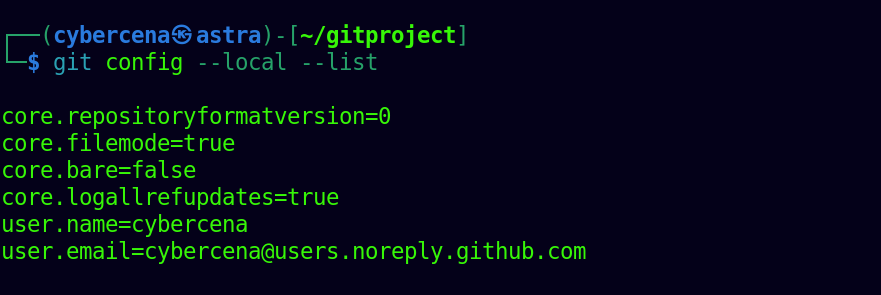
View Git Configuration
Last updated