Intro to Git and GitHub
Version Control
Version Control is a system that records changes to file(such as source code, documentation, or designs) over time, so you can track history, collaborate with others, and restore previous versions when needed. It's like a digital history book for our project. Every update, correction, or experiment is saved as a version that we can revisit anytime.
Importance of Version Control
Tracks History : it keeps a detailed log of who changed what, when and why.
Collaboration Made Easy : Multiple Developers can work on the same project without overwriting each other's work.
Error Recovery : Mistakes or broken code can be rolled back to a working version.
Experiment Safely : Developers can create branches to try new features without affecting the main project.
Efficient Project Management : Helps in organizing, reviewing, and merging code in a structure way.
Industry Standard : Used by almost all software teams, open-source communities, and enterprises to manage codebases.
Centralized Vs Distributed Version Control System
Code storage
On central server only
On every developer’s machine
Offline work
❌ Not possible
✅ Fully possible
Risk if server fails
❌ High
✅ Low (everyone has backup)
Speed of operations
Slower
Faster
Examples
SVN, CVS
Git, Mercurial
What is Git ?
Git is a distributed version control and source code management system. It helps developers track and manage different versions of a project’s source code. Git also makes it easier to collaborate with others, maintain a history of changes, and even serve as a backup for source code.
Version : different iteration of same things
Do you know ?: In 2005, the Linux kernel development team faced a challenge. They needed a fast, reliable, and distributed version control system after a conflict with their then-current tool, BitKeeper. Linus Torvalds, the creator of Linux, took on the task and developed Git.
Why do we need Git ?
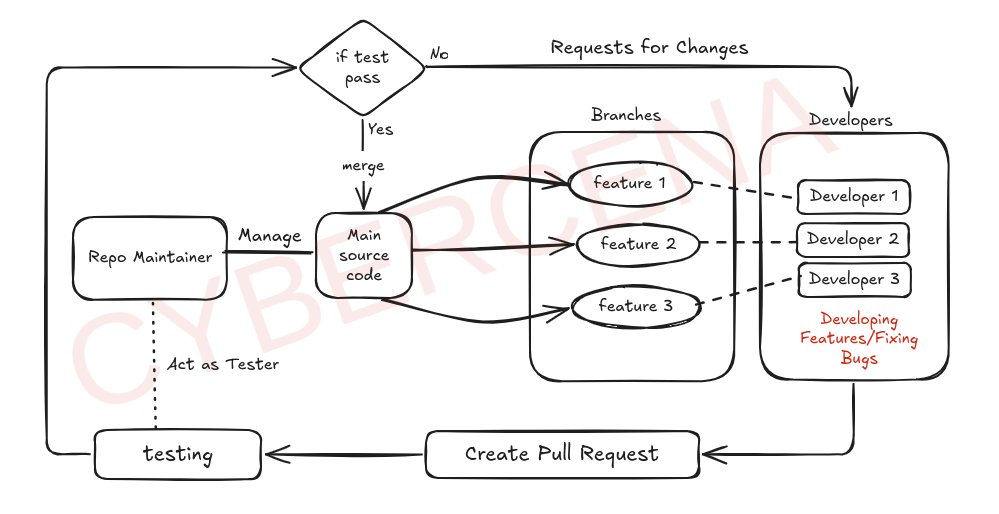
It Provides Version control
It provides the branching
It offers collaboration
It offers merging
It provides Backup & Safety
What is GitHub ?
GitHub is a web-based platform used for version control and collaborative software development. It allows developers to store, manage, and track changes to their code using Git, a distributed version control system.
What we can do in GitHub ?
Create a repository
Start a new project
Clone a repository
Download the project to work on it locally
Commit changes
Save a snapshot of your changes
Push to GitHub
Upload your changes to the GitHub website
Fork a repo
Copy someone else’s project to make your own version
Open a pull request
Suggest changes to someone else’s project
Merge code
Combine changes from different contributors
Differences Between Git and GitHub
Feature
Git
GitHub
Type
Version Control System (VCS)
Cloud-based Git repository hosting service
Purpose
Track and manage changes to files/code
Host, share, and collaborate on Git repositories
Created By
Linus Torvalds (2005)
Tom Preston-Werner, Chris Wanstrath, etc. (2008)
Owned By
Open-source community
Microsoft (since 2018)
Works Offline
Yes
No (requires internet access)
Installation
Installed on your local machine
Accessed via web browser (no installation needed)
Primary Use
Local version control
Remote collaboration and repository hosting
User Interface
Command Line / GUI Tools
Web Interface (plus GitHub Desktop)
Collaboration Tools
Not built-in (only local operations)
Pull requests, issues, discussions, teams
CI/CD & Automation
Not included
Available via GitHub Actions
Security
Local only (you control everything)
Offers access control, authentication, and permissions
Last updated