Git Repository
Repository
A Git Repository is a storage space where your project and its complete version history (all changes to files over time) are tracked by Git, a Version Control System. It is often known as Repo.
There are Two kinds of Git Repository :
Local Repository : Store on your Computer
Remote Repository : Hosted Online (e.g., GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket)
Components of Git Repository
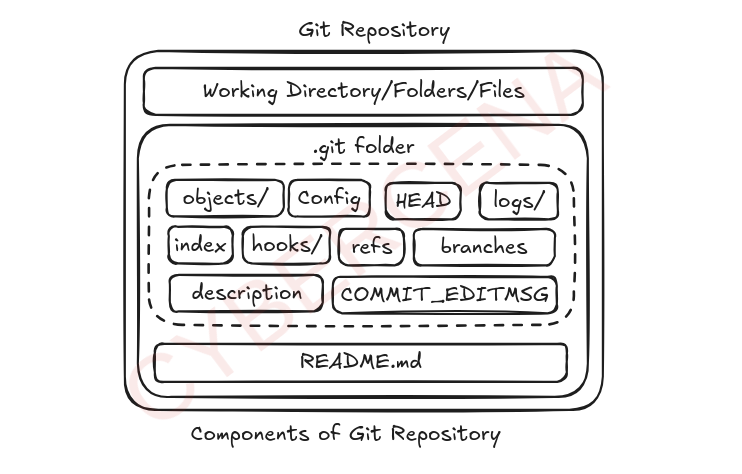
Working Directory / Folders / Files
Directory
The actual project files you're working on — source code, assets, etc. These can be tracked or untracked by Git.
.git/
Hidden Folder
The heart of the Git repository — contains all the internal data Git needs to manage version control.
objects/
Folder
Stores all Git objects: commits, trees, and blobs. It's Git’s database. Each object is referenced by its hash (SHA-1 or SHA-256).
config
File
Stores local repository configuration (e.g., user info, remotes). View with git config --list.
HEAD
File
A pointer to the current branch or commit. Git uses this to know what you're working on.
logs/
Folder
Keeps track of reference updates (e.g., commits, rebase, reset). Used for git reflog.
index
File
The staging area — holds a snapshot of your next commit. It tracks what will go into the next commit.
hooks/
Folder
Contains scripts that run automatically on Git events like commits or merges (e.g., pre-commit, post-merge).
refs/
Folder
Stores pointers to commit objects, like branches (heads/), remotes, and tags.
branches/
Folder
(Legacy) Used in older Git versions for branch references. Now mostly empty or unused.
description
File
Used by Git web interfaces (like GitWeb) to describe the repo. Not relevant for Git operations.
COMMIT_EDITMSG
File
Stores the commit message from the most recent commit. Git opens this during git commit.
README.md
File
A user-defined file, not part of Git internals. Typically contains documentation or info about the project.
Initialize Git Repository
Step 1 : Create and Navigate to Directory
create a folder with a project name you want to work,

Step 2 : Initialize the Git Repo
Run the command inside Git Repo,
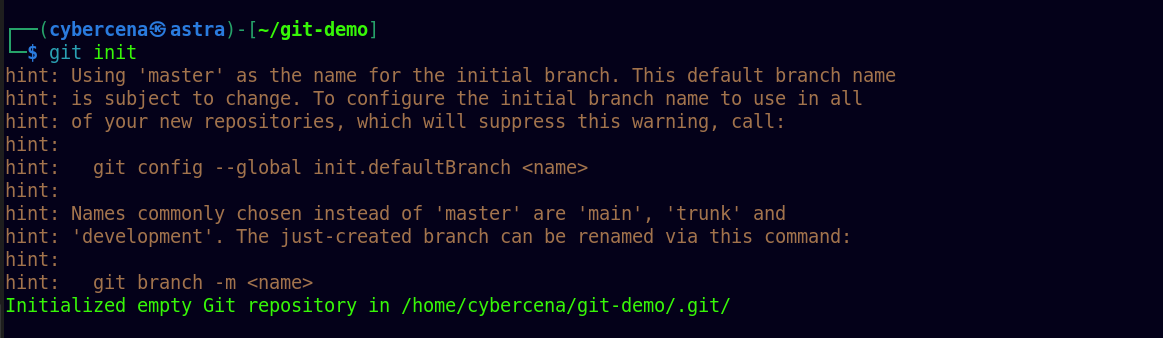
check if it contains, hidden folder
.gitto confirm if the repo was created or not.
if it Repo was created successfully, it should include
.gitfolder.

Step 3 : Configure the Git Repo
You need to configure the Git repository to publish it remotely to GitHub.
There are two ways to Configure Git
Locally : for a specific repository
Globally : for all repositories on your system
Last updated